
Choose the Right Sports Medicine Expert
July 7, 2020
By Christina Eyers, Ed.D., AT, ATC
Henry Ford Health System
If you're an athlete, chances are you'll require specialized care from a health professional during your career.
Confused about the differences between athletic trainers, sports medicine physicians and exercise physiologists, among other experts? You're not alone!
Each of these professionals has different levels of training, expertise and certifications, but the care they provide often overlaps. That's one reason why they often work together.
Sports Professionals Defined
Caring for athletes isn't always clear-cut. In fact, most athletes require a full team of professionals working in concert to stay at the top of their game. Yet confusion remains about which professionals you need to see for training, injury prevention, and recovery and treatment after an injury.
Each type of professional has its own set of experience, training and certifications. Here’s how they measure up:
· Sports medicine doctor: Sports medicine physicians are typically trained in orthopedic surgery, primary care or emergency medicine. These professionals have medical degrees as well as specialized training in sports medicine, including the prevention and treatment of injury. In addition to caring for conditions ranging from concussion to head colds, sports medicine physicians also focus on helping people return to sports safely and effectively after illness or injury.
· Athletic trainer: Athletic trainers take care of athletes from prevention through rehabilitation. In collaboration with a physician, these professionals offer insights that help minimize risk and prevent injuries. They evaluate athletes and provide immediate care and treatment, sometimes even on the sidelines. They also provide rehabilitation and reconditioning after an injury or illness.
· Exercise physiologist: Exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on the muscular, cardiovascular, and sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. They examine functional capacity and strength due to endurance training or strength training. These professionals may also test athletes for VO2max (your oxygen volume while training) and body composition (the ratio of fatty mass to lean mass).
· Physical medicine and rehab physician: These professionals treat a variety of medical conditions that affect the brain, spinal cord, nerves, bones, joints, ligaments, muscles and tendons. They take the whole body into account to pinpoint problems and enhance performance without surgery.
· Physical therapist: Physical therapists diagnose and treat individuals of all ages with conditions that limit their ability to move and perform daily activities.
Other Specialized Professionals Who Care for Athletes
In addition to the health care professionals described above, athletes may meet with a host of experts, including:
· Nurses and medical assistants
· Occupational therapists
· Cardiologists
· Neurologists
· Behavioral health specialists
· Dietitians
· Complementary medical practitioners, such as acupuncturists and chiropractors
None of these individuals are "fitness professionals," a term nearly anyone can use to describe a range of professional activities. Rather, these sports medicine experts are part of a comprehensive team that includes at least one physician. They are each licensed by the state to provide specialized care to athletes.
Personal trainers, on the other hand, focus on helping people find their way around the gym, hold them accountable to achieve their goals and help new exercisers and seasoned fitness enthusiasts stick to a workout regimen.
If you're an athlete, you need a team of health professionals who can provide comprehensive care to reach your highest potential.
Christina Eyers, Ed.D., AT, ATC, is the Director of Athletic Training & Community Outreach with Henry Ford Sports Medicine.
Want to learn more? Henry Ford Health System sports medicine experts are treating the whole athlete, in a whole new way. From nutrition to neurology, and from injury prevention to treatment of sports-related conditions, they can give your athlete a unique game plan.
Visit henryford.com/sports or call (313) 972-4216 for an appointment within 24 business hours.
Coaches Guide to Nutrition: What are Macros?
April 30, 2024
Planning your meals and snacks shouldn’t be challenging.
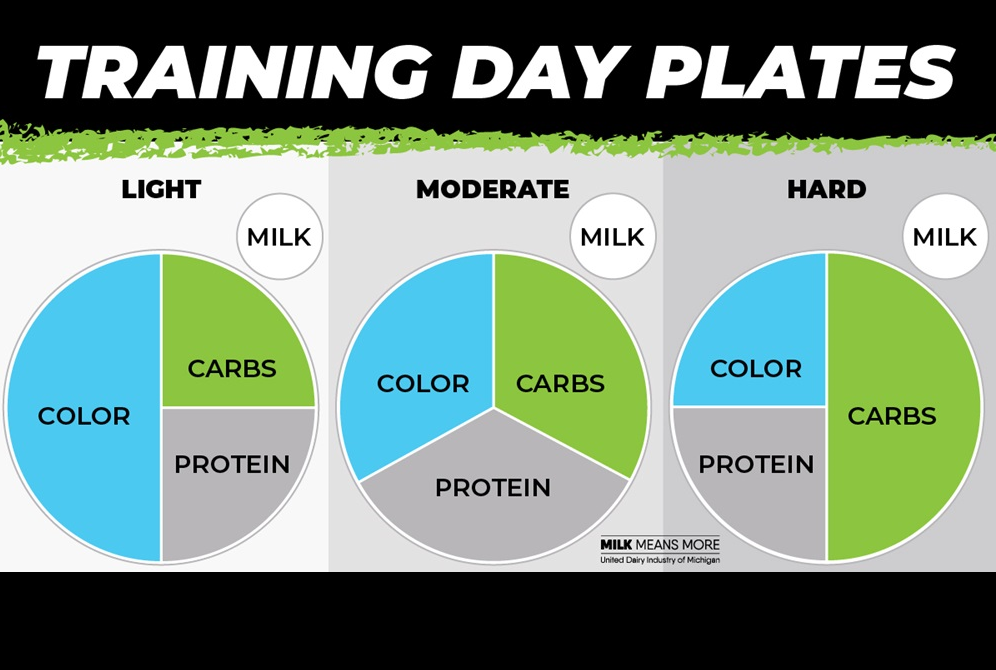
Break foods down into three categories: Carbs (energy), Protein (build and repair muscles), and Color (vitamins, minerals).
Adjust your plate based on your level of activity that day. Remember that your body needs carbohydrates like grains, fruits and vegetables for muscle fuel.
On hard training days, up to half of your plate should be carbs. On a recovery or rest day, make a quarter of your plate carbs.
Plan your meal
Check out these examples for your day’s main meals:
- Overnight oats with fruit
- Egg wrap with spinach, cheese and salsa
- Cereal with fruit and milk topped with nuts
- Smoothie made with milk, fruit, spinach and oats
- Don’t forget about school breakfast!
Lunch
- Turkey roll-up with cheese, tomato and lettuce, fruit and milk
- Grilled cheese sandwich, tomato soup, small salad, milk and pear
- Large salad with your choice of berries, grilled chicken, cheese and vinaigrette dressing, garlic bread and milk
- School lunches are made with student nutrition in mind!
Dinner
- Pasta with chicken, pesto, tomatoes and peas with milk
- Shrimp or tofu fajita bowl with brown rice, peppers, onions and shredded cheese. Add guacamole and plain Greek yogurt instead of sour cream.
- Cheeseburger made with 90 percent lean beef or turkey on a whole grain bun with lettuce and tomato and a glass of milk. Add baked sweet potato fries on the side.
Information above is excerpted from UDIM’s A Coach’s Guide to Nutrition.



